About the red planet
Mars is the fourth planet in our solar system, also known as the red planet because of its color. The origin of planet’s reddish color is in the Martian soil covering the planet, which constitutes mainly of silicon dioxide and ferrite oxide, the latter being the cause for this distinctive color. The Martian surface, covered with regolith, dust, resembles a desert like environment, devoid of life, with extreme negative temperatures and an atmosphere that does not allow for life to flourish. In addition to that, Mars has many interesting geological features, which indicate, that the planet once was alive, that long time ago there was flowing water and the planet was geologically active. However, the question of past life remains and the planet is yet to be fully explored.
The origin of the name

The planet’s name dates back to the time of Roman Empire. Mars was named after the Roman god of war (Mars), since the color of the planet represents the blood spilled during a war. And accompanying the god of war are two war horses, Deimos and Phobos, pulling Mars’s war cart. These names are also the names of the Mars’ two moons, as the moons represent these two horses. The moons represent fear and panic, which is present in every battle, war. Other countries named Mars in a similar fashion, giving it a name such as The red one in Egypt.
Some facts
As mentioned before, Mars is the fourth planet in our solar system, located between Earth and Jupiter. It’s distance from the sun is 1,5-times bigger than Earth’s distance from the sun, or more precisely it’s distance from the sun equals 1,524 AU (astronomical units) or 228 million kilometers. As a result of it’s longer distance, the orbital period of Mars differs from the Earths orbital period by a large margin.
To point out some other interesting facts about Mars, it’s gravity equals about one third of Earth’s and the temperatures on Mars range from as low as -140 °C to, though very rarely, 20 °C. The cause for such low temperatures is mainly the lack of a proper atmosphere, which has disappeared as a result of solar winds and Mars lacking a strong magnetic field as opposed to Earth which has a strong magnetic field and which protects the planet from the solar winds.
In the table below I have written down some more numbers about Mars, which I found interesting.
| Average distance from the sun | 227.936.637 km |
| Orbital period | 686.96 days |
| Average orbital speed | 24,007 km/h |
| Equatorial diameter | 6.804,9 km |
| Polar diameter | 6.754,8 km |
| Mass | 6,4 * 10^23 kg |
| Gravitational acceleration | 3,69 m/s^2 |
| Escape velocity | 5.027 km/s |
| Martian day length | 24,62 h |
| Inclanation | 25,19° |
| Albedo | 0,17 |
| Surface temperature | 133 – 293 K -140 °C – 20 °C |
The atmosphere
The atmosphere on Mars, though almost non-existent, is one of the reasons why life on Mars in its current state is impossible. It lacks oxygen, and is composed mainly of CO2, which might make one wonder, why the planet is so cold, since CO2 is a known cause of global warming. The reason lies in the thickness of the atmosphere, as the atmospheric pressure on Mars ranges from 0,7 to 0,9 kPa (while on Earth the it is 101,3 kPa at sea level) – which means the atmosphere on Earth is about 120-times denser than on Mars. In addition to this, as mentioned, the temperatures on Mars range from as low as -140 °C to only 20 °C. The combination of these properties make the planet’s atmosphere one of the main reasons for the planet’s uninhabitability.
| Atmospheric pressure | 0,7 – 0,9 kPa |
| CO2 | 95,32 % |
| N2 | 2,7 % |
| Ar | 1,6 % |
| O2 | 0,13 % |
| H2O | 0,03 % |
Martian surface
The Martian surface is mainly known for its red surface, but upon close inspection, we can see that its surface also consists of other colors such as gold, brown and orange colors. The primary reason for this color scheme is the high abundance of ferrite (iron) ores in the rocks and Martian soil (regolith). From an outsider’s perspective the planet also often appears red because of the common Martian winds, which sweep the planets surface, sometimes even for months. Another interesting fact about the planet is that the size of its surface is roughly equal to the size of our planet’s surface, even though the diameter of Mars is about twice as small as Earth’s.
Despite of the planet’s current geological inactivity, the planet certainly does not lack interesting geological features, which are the result of past volcanic activities, meteors and atmospheric phenomena. The planet is full of canyons. The largest system of canyons is called Valles Marineris, spanning over 4800 km and with a maximum width of 320 km, is 10-times bigger than the famous Grand Canyon in America. In addition to that Mars is the home to the largest, though inactive, volcano in our solar system called Olympus Mons, with a whopping height of 22 km, surpassing the Mt. Everest by a large margin!
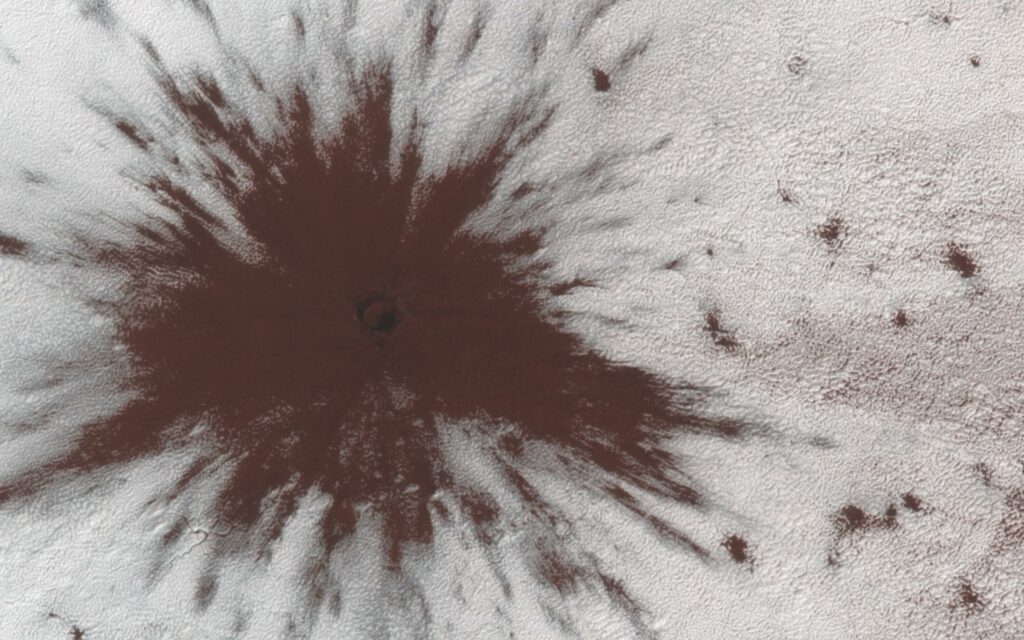

And lastly, the presence of water on Mars, which at the first glance the planet is almost devoid of. However, it has been proven that Mars once has flowing water, which shaped its dry river beds, deltas and lake craters. Today however, Mars posses no flowing water, as its atmosphere and temperatures do not allow that. As a result, water is only found in the form of ice on the south and north poles of Mars as well as in the regolith in, however, very small quantities.
Below is a 360° video of the Martian surface recorded by the Perseverance Rover after its landing on the red planet.
![The Past, Present and Future of Mars [Part 0]](https://davidblog.si/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Mars-Website-banner-1-1024x576.jpg)